Companies need to deal with risk to run smoothly. There are many types of risks, like economic and competitive challenges. Strategic risk management helps improve confidence from those involved and boosts business success. This process involves looking at risks, figuring out how likely and severe they are, then taking steps to reduce them.
Key Takeaways
- Risk management is the systematic process of identifying, assessing, and mitigating threats or uncertainties that can affect an organization.
- Effective risk management can protect an organization’s reputation, minimize financial losses, encourage innovation and growth, and enhance decision-making.
- Organizations that embrace strategic risk management are more likely to achieve better business outcomes and faster revenue growth.
- Risk management involves analyzing the likelihood and impact of risks, developing strategies to minimize harm, and monitoring the effectiveness of those measures.
- Businesses must proactively manage a variety of risks, including operational, financial, and strategic risks.
Also Read : What Are Financial Markets And How Do They Function?
Understanding Risk Management
Risk management means spotting, measuring, and handling dangers to a business’s money, profits, and activities. These dangers come from many places, like not knowing costs, legal risks, tech problems, mistakes in planning, accidents, and nature’s fury.
Also Read : What Does An Insurance Broker Do?
Definition of Risk Management
Risk management is the careful method of spotting, checking, and lessening risks that might stop a company from reaching its goals. It looks at how likely and how big a risk is, then plans ways to cut down or handle it well.
Types of Risks
Businesses deal with all sorts of risks, from how they work day-to-day, to their money, strategies, following rules, and what people think of them. These dangers change a lot depending on the business’s field, size, and where it is.
Also Read : How Does Diet Affect Kidney Disease?
Causes of Strategic Risk
Strategy Execution says strategic risk usually comes from three things: needing to grow, fitting in with other businesses, and using information correctly. These risks might involve how a company works, losing asset value, fighting off competition, or risks to its reputation.
Also Read : Top 10 Healthy Eating Tips You Need To Know
Importance of Risk Management

Risk management is essential for safeguarding against big losses. It shields organizations from various harms such as financial setbacks and damage to the organization’s reputation. For example, good risk management helped Delta Airlines tackle a major computer outage in 2016. This proactive move saved their reputation.
It also cuts down on financial losses. In 2021, workplace misconduct cost US companies about $20 billion. Plus, it helps boost innovation and growth. Organizing how to tackle competition risks allows companies to grow. It also lets employees take calculated risks within set boundaries, fostering innovation.
Also Read : What Is Credit Risk And Why Is It Important In Finance?
Risk management leads to better decision-making too. It provides data and steps to evaluate what might go wrong. This helps organizations choose actions that match their ambitions, resulting in the benefits of effective risk management in the long run.
Risk Management Strategies

Organizations use different risk management strategies to deal with threats and uncertainties. The main five are: risk acceptance, risk transference, risk avoidance, risk reduction and loss prevention, and risk sharing.
Risk acceptance means an organization knows the risks of a situation but decides the benefits are worth it. Risk transference passes the risks to someone else. This can be done through insurance or by outsourcing work to another company.
In risk avoidance, an organization takes steps to stop a risk from happening. They might stop certain activities or put in strong safety measures. Risk reduction and loss prevention aims to lessen the damage if a risk comes true. This includes having backup plans or quick response teams.
With risk sharing, risks are spread out among the whole team. Everyone takes a part in managing and dealing with threats. This could mean working together or sharing resources.
| Risk Management Strategy | Description |
|---|---|
| Risk Acceptance | Consciously deciding to accept the risks associated with a particular situation, determining that the benefits outweigh the potential consequences. |
| Risk Transference | Shifting the risks to another party, such as through insurance or outsourcing certain activities to a third-party provider. |
| Risk Avoidance | Taking proactive steps to prevent or avoid a particular risk from occurring in the first place, such as eliminating high-risk activities or implementing robust controls and safeguards. |
| Risk Reduction and Loss Prevention | Minimizing the impact of risks that do materialize, such as implementing backup systems, business continuity plans, and emergency response procedures. |
| Risk Sharing | Distributing the risk across the entire team or organization, rather than concentrating it in one area, through collaboration, resource pooling, or shared responsibility for managing potential threats. |
Organizations should look closely at different risk management strategies. They must choose the best one for their risk level and business goals.
Principles of Risk Management

Risk management has five main parts: identifying risks, checking them out, controlling them, covering costs, and handling claims. These steps help any organization deal with the risks and chances that come along.
Risk Identification
Risk identification is first. It means knowing what can go wrong by looking at the business and its surroundings. This step is key to making sure all risks are dealt with properly.
Risk Analysis
After spotting risks comes risk analysis. It’s about figuring out how likely and how bad each risk can be. This involves using different methods to find out which risks need the most attention.
Risk Control
Risk control is next. It’s about finding ways to lower or get rid of risks. This might mean making backup plans, improving security, or changing processes to avoid problems.
Risk Financing
Risk financing looks at setting aside money to cover risk costs. Organizations might buy insurance or save money to handle risks. This ensures the business can stay afloat even when faced with financial hits.
Claims Management
The last part is how to manage claims. Once a risk hits, dealing with claims is vital. This involves setting clear processes, keeping good records, and working with others to solve claims quickly, lessening their impact.
The Risk Management Process
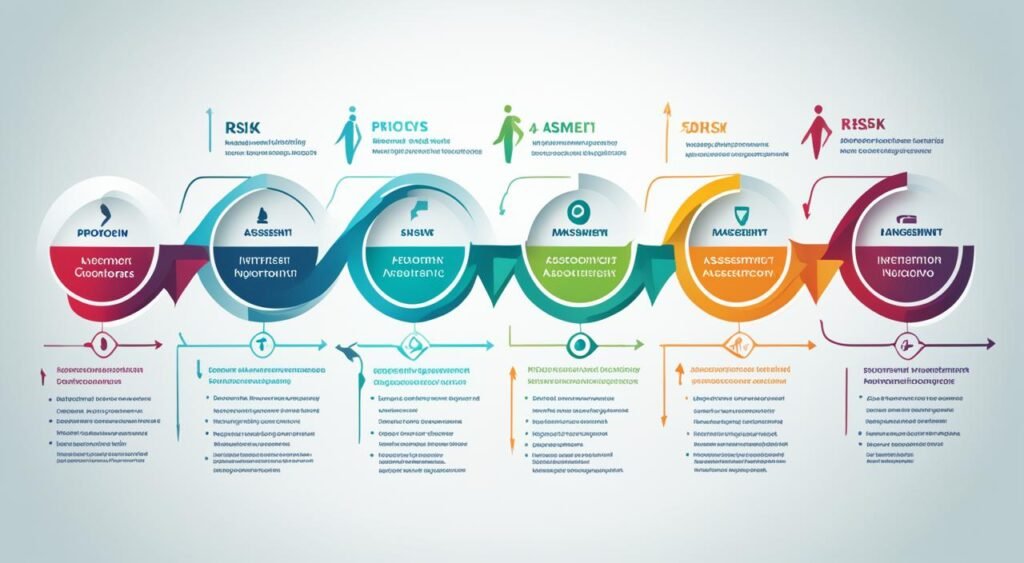
The risk management process is how businesses spot, figure out, and lower dangers. These dangers could hurt how a company runs, its money, or its success. This method has four main steps. They help companies deal with risks before they cause harm.
Identify the Risks
The first step is to identify the risks that your company could face. This means looking at what might go wrong, like problems from inside or outside your company. For example, you’d check out things like the market, what’s happening in your industry, how your company works, and your finances. Risk managers put together a list of possible risks after looking at all these areas.
Assess the Risks
After listing the risks, the next move is to assess the risks. This is about figuring out how likely each risk is to happen and how bad it could be if it does. By doing this, businesses decide which risks to focus on. They pinpoint the ones that could hurt the most. They use key risk indicators (KRIs) to keep an eye on these big risks.
Treat and Manage the Risks
Now, it’s time to treat and manage the chosen risks. This could mean cutting down or getting rid of them. Companies might put new rules in place, change how they do things, or pass the risk to another group. Experts in risk management make sure these plans are put into action well. They make sure these steps really lower the risks.
Review and Monitor
The last step is to review and monitor how well things are working. Companies keep track of their plans and how they’re doing using KRIs. They change their approach if needed to keep risks under control. This ongoing check helps companies handle new risks that might come up in the future.
Risk Management Examples

Organizations use different risk management strategies to tackle their issues. This includes dealing with compliance risks, safety risks, and information security risks.
Compliance Risks: Companies must keep up with changing rules and laws. They need to watch for new requirements, check their risks, and set rules to follow. Doing this stops companies from getting fined or losing their good name.
Safety Risks: It’s on businesses to keep everyone safe, from staff to clients. They should find dangers, see how bad things could be, and plan to make things safer. This could include teaching staff safety, keeping tools in good shape, and having plans for emergencies. Stopping accidents isn’t just good for people, it keeps a company on the right side of the law.
Information Security Risks: With everything digital, there are more chances for hackers and other dangers. To stay safe, companies need good online security, staff who know how to stay safe, and plans if something goes wrong. This way, they can keep secrets safe, keep working if there’s a problem, and keep customers trusting them.
Tackling these risks head-on with smart management helps companies be stronger and better ready for the changes and challenges ahead.
Risk Management Tools

Risk management means using different tools to find, study, and lessen dangers. Some top tools are SWOT analysis, root cause analysis, risk register, probability and impact matrix, and brainstorming.
SWOT Analysis
SWOT analysis looks at what’s good and bad inside and outside a company. It helps find which tools are best to use. This way, they can deal with challenges and make the most of what they do well.
Root Cause Analysis
Root cause analysis goes to the main problem’s source. It’s more than just fixing what’s on the surface. By using this tool, organizations can fight risks in a lasting way.
Risk Register
A risk register keeps track of possible project or organization dangers. It details each risk’s chances, effects, and who’s in charge. This helps keep an eye on these dangers and fight them better.
Probability and Impact Matrix
The probability and impact matrix sorts risks by how likely and harmful they are. It tells which ones need the most attention. Then, they can focus on fighting the big risks first.
Brainstorming
Brainstorming brings a team together to think up fresh ideas. This helps deal with problems in engaging ways. It’s a great tool to discover new ways to lessen risks.
Also Read : All You Need To Know About Renters Insurance
Enterprise Risk Management (ERM)
Enterprise risk management (ERM) looks at risks in a broader and more proactive way than traditional methods. ERM considers risks in a holistic way across the whole organization. It checks how different risks affect each other and the overall impact they might have together. Traditional methods tackle risks in separate parts, but ERM uses a team approach. This team includes people from different parts of the company. They work together to find, measure, and reduce risks in line with the business’s main goals. ERM sees managing risk as a way to help the business, not just as a necessary cost.
| Traditional Risk Management | Enterprise Risk Management (ERM) |
|---|---|
| Focuses on individual risks in silos | Takes a holistic, organization-wide view of risk |
| Reactive approach to risk | Proactive, strategic approach to risk management |
| Primarily manages financial and operational risks | Addresses a broader range of risks, including strategic, compliance, and enterprise-wide risks |
| Risk management is viewed as a cost center | Risk management is seen as a strategic enabler |
The main difference between the old way and ERM is how they see and handle risks. ERM takes a comprehensive, holistic view of risks. It links risk management to the company’s strategy and goals. This helps businesses expect, handle, and even use wide-reaching risks. Instead of just reacting to single risks, ERM prepares companies to face all risks together.
Conclusion
Risk management is key for all companies now. It guards a company’s image, limits money losses, sparks new ideas, and betters decision-making. More firms see risk’s big picture and weave it into their whole strategy.
Smart risk handling benefits are many. Firms can dodge reputation hits and undesired situations. Risk management helps cut money loss and faces off competitive risks, making room for fresh thoughts. Mostly, it turns data into smart choices and lays a plan for handling what-ifs.
Looking ahead, risk management will change as businesses face new unknowns. They will need smart, tech-filled strategies that spot, grade, and face risks in the moment. Top players later will have risk at their core, making it a tool for lasting achievement.





