As anyone living with type 1 diabetes can attest, managing it can be a challenging endeavor. Maintaining optimal health requires constant awareness of your body’s needs. Being proactive about taking control of your own wellbeing is key to living well with type 1 diabetes; so here are 10 tips to help manage and live a healthier life with this condition.
Tips To Help You Live A Healthy Life These tips will empower you to take control of your health and well-being, from learning how to count carbohydrates to monitoring blood sugar levels closely. With access to accurate information, smart choices can lead to improved blood sugar management, energy levels, and overall wellbeing – giving you control of type 1 diabetes for good! Take action now.
Also Read : 6 Must-See Destinations In France For An Unforgettable Vacation Experience
Understand Your Type 1 Diabetes

Type 1 diabetes occurs when the pancreas stops producing enough insulin, an essential hormone necessary for turning glucose (blood sugar) into energy for energy use by your body. High levels of blood glucose can be detrimental to health; there’s no known cure, but managing your condition through diet, exercise and medications is possible.
Type 1 diabetes usually appears during childhood or adolescence, while type 2 usually manifests later. Type 2 is most frequently caused by being overweight and not getting enough physical activity; type 1 produces little to no insulin at all.
Also Read : 6 Proven Strategies To Overcome Burnout And Recharge Yourself
Tips To Help You Live A Healthy Life
1) Learn To Count Carbohydrates
People living with type 1 diabetes must carefully manage their carbohydrate consumption to manage blood sugar levels. Carbs are the main source of blood sugar (glucose) production in their bodies and can be found in many foods and beverages such as fruits, vegetables, grains, milk products, beans legumes and sugars – they’re listed on food labels!
Also Read : How To Balance Your Blood Sugar Levels Naturally – A Comprehensive Guide
When counting carbohydrates, be sure to include all sources of natural sugar such as fruits and vegetables. Hyperglycemia occurs when your body lacks enough insulin to utilize glucose as energy source and uses too much of its stored glucose reserves as fuel instead.
Also Read : 10 Must-See Places To Visit In Sweden For A Memorable Vacation Experience
2) Monitor Your Blood Sugar Levels
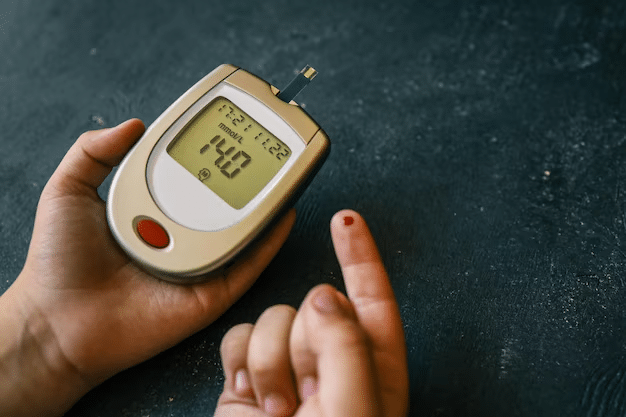
Accurate monitoring of your blood sugar levels is vital to effective diabetes management. Blood sugar can fluctuate throughout the day depending on what you eat and physical activity levels; people living with type 1 diabetes often use blood glucose monitoring devices to check their levels throughout their day – there are various kinds of devices to choose from so picking out one tailored specifically to you is key.
Also Read : 6 Natural Ways To Lower High Blood Pressure And Manage Hypertension
There are different kinds of blood glucose monitors, such as finger-stick devices, continuous glucose monitors, handheld devices and continuous glucose monitors. Finger-stick devices use lancets to swab out small drops of blood from your fingertips while handheld ones measure a drop from one finger or piece of skin from multiple locations on your fingertip or from another source.
3) Get Regular Exercise
Exercise regularly is key to helping maintain healthy blood sugar levels and leading a balanced life. Most people living with type 1 diabetes can significantly lower their blood sugar with regular physical activity; it is recommended to consult with healthcare provider prior to beginning any new fitness regimes.
Exercise can help you improve blood sugar control, strengthen muscles, lower your risk of heart disease and help you shed excess pounds while relieving stress. Particularly beneficial are aerobic and strength training exercises as these may provide opportunities to meet other people who share similar experiences in managing their condition. You may want to join a local diabetes exercise class for added support as you navigate managing this chronic illness
4) Eat Healthy Foods
Eating healthy foods is key to controlling blood sugar and managing weight. Eating right can also promote healthy blood lipids levels, blood pressure levels and may prevent some cancers. Eating healthily for those living with type 1 diabetes can be challenging as it’s hard to know exactly which food contains how many carbs
Many diet books are available that are tailored towards people with diabetes, as well as online resources that can help you learn how to manage your diet by counting carbohydrates. Try to include vegetables, fruits, whole grains, and low-fat dairy products in your diet. Avoid foods that are high in fat, protein, and/or carbohydrates.
5) Practice Stress Management

Stress can have an adverse effect on blood sugar levels, so it’s essential to find ways to effectively manage stress. There are various means at your disposal – exercise, relaxation techniques and social support among them – for effectively dealing with your anxiety. Learning when you’re feeling stressed and taking immediate steps to alleviate it are also key steps toward managing it more effectively; healthy ways include talking to friends or joining support groups as ways of relieving it.
If you are feeling overwhelmed by stress, take some time out from daily activities to rest and relax. People living with type 1 diabetes are particularly prone to experiencing it due to managing its condition; therefore it’s essential that they learn how to effectively handle stress management if their blood sugar levels rise as a result. Proper stress management can actually contribute to living a healthier life!
6) Stay Hydrated
Staying hydrated is one of the key ways to control blood sugar levels, as water plays a significant role in metabolism of carbohydrates, fats and proteins. Staying hydrated allows your body to break down food more effectively while using nutrients efficiently; furthermore it flushes waste out of your system, helping prevent kidney stones and many forms of kidney diseases.
People living with type 1 diabetes often fail to drink enough water. This can lead to dehydration and cause blood sugar levels that are too high, requiring you to adjust them by increasing insulin use or eating too many carbs. Make sure you drink sufficient fluid throughout the day in order to stay hydrated. Drink plenty of fluids throughout your day in order to remain properly hydrated!
7) Take Medication As Directed
As with taking any medication, taking yours as directed can help control blood sugar levels. It is vital that you follow the directions from your healthcare provider when taking medications in order to achieve effective blood sugar management and avoid complications caused by high levels of blood glu.
If you are taking blood glucose-lowering medication, be sure to eat healthily and exercise regularly; this will assist the medicine in working more effectively. If your blood sugar levels continue to fluctuate excessively, contact your healthcare provider regarding adjusting the medication – but be patient, as it may take time before your medications work perfectly for you.
Sleep is crucial to overall health, including blood sugar control. Studies indicate that people who don’t get enough rest have higher blood sugar levels and potentially serious health complications as a result of not enough restful slumber.
8) Get Enough Sleep
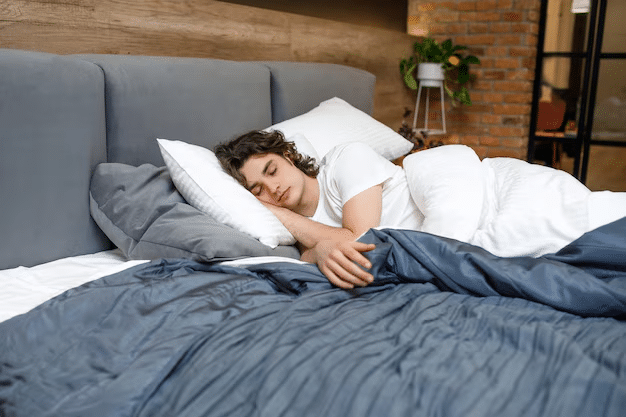

Sleep is important for overall health, including blood sugar control. Studies show that people who don’t get enough sleep have higher blood sugar levels, which can lead to serious health complications.
When you get enough sleep, it helps maintain a balanced level of hormones, including insulin, which is critical for blood sugar control. When you don’t get enough sleep, your body releases too much insulin, which lowers your blood sugar.
9) Get Regularly Check Up
Visit your physician at least twice annually and learn your numbers – cholesterol, blood pressure and A1c. Get a full eye exam every year as well as visiting a foot doctor regularly in case there are foot ulcers or nerve damage issues; check average blood sugar levels against normal range and how close to ideal they may be.
After first being diagnosed, regular assessments should take place every three months for six months until you become stable. Your blood pressure and weight will be assessed, along with self-care plans and medications being reviewed by either a GP or diabetes nurse.





